Brazilian Niobium Iron Powder Chinese Niobium Iron Powder Ferrous Niobium Fenb50 Nb Iron Powder 60 Niobium Iron Powder 65
Description
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | Brazilian niobium iron powder Chinese niobium iron |
| HS Code | 7806009000 |
| Production Capacity | 500 / Ton |
Product Description

Description of Product
Product name: Niobium iron powder
Ingredient content: Nb50~70%
Application: Suitable for welding materials, powder metallurgy and other industries
| Chemical Composition: | /Size: | ||
| Nb | 65.08% | S | 0.03% |
| Ta | 0.12% | P | 0.12% |
| C | 0.13% | Al | 2.1% |
| Si | 2.13% | W | 0.06% |
Niobium is a high melting point metal, steel-gray, with an atomic weight of 92.9064, an outer electronic structure of 4d5s, a melting point of 2467ºC, a boiling point of 4740ºC, and a density of 8.6g/cm3 (20ºC). FIG. 1 shows the equilibrium phase diagram of Fe-niobium binary system. There are two eutectic points and a MgZn2 type of εNbFe2. The two eutectic points are located at Nb11.6%, 1360ºC and Nb at about 55%, 1560ºC, respectively. Industrial iron niobium (FeNb60) has a melting temperature range of 1520 ~ 1600ºC and a density of about 8.0g/cm3.
Ferrous niobium is mainly used for smelting high temperature (heat resistant) alloy, stainless steel and high strength low alloy steel. In stainless steel and heat-resistant steel, niobium forms stable niobium carbide with carbon in steel. Distributed uniformly in the grain boundary of steel, prevent the grain growth of steel at high temperature, refine the structure of steel, and improve the strength, toughness and creep performance of steel. The chemical affinity of niobium and carbon is much greater than that of chromium and carbon. Therefore, when there is niobium in stainless steel, chromium carbide precipitation can be prevented in the grain boundary of steel, thus improving the corrosion resistance of steel. The niobium and nitrogen in steel form stable niobium nitride, which improves the surface corrosion resistance of steel. The niobium and oxygen in the steel form stable niobium oxide, so that the surface of the steel form niobium oxide film, which can prevent the oxygen from spreading to the interior and play the role of oxidation resistance. The addition of Nb0.015% ~ 0.05% to carbon steel can refine the microstructure and make the steel have good formability and welding performance. Niobium has a strong inhibiting effect on the recrystallization of steel austenite, which can effectively control the rolling of steel at higher temperature, and the strengthening and toughening effect of controlled rolling is very significant. So the amount of niobium as a microalloying element in carbon steel is greatly increased. The amount of niobium used in microalloys in the United States was only 1.9 percent of the total niobium consumption in 1959, but increased to 68 percent in 1988.
Niobium plays the role of solid solution strengthening and carbide precipitation strengthening in superalloy, which can improve the yield strength and surface stability of superalloy. The weight of niobium is one of the lighter refractory metals, and it is one of the factors for the extensive use of superalloys. Niobium - Ni alloy as an additive in nickel - based superalloy is mainly used to produce 718 alloy. The coercivity of permanent magnet alloy can be improved by adding niobium.
The addition of niobium to cast iron is helpful to spheroidization and the formation of pearlite structure. It is used to breed and refine the structure of the casting. Niobium can improve the strength, toughness, hardness and service life of castings at high temperature. Iron niobium is used as the solder component to improve the welding quality.
The production process editor reports
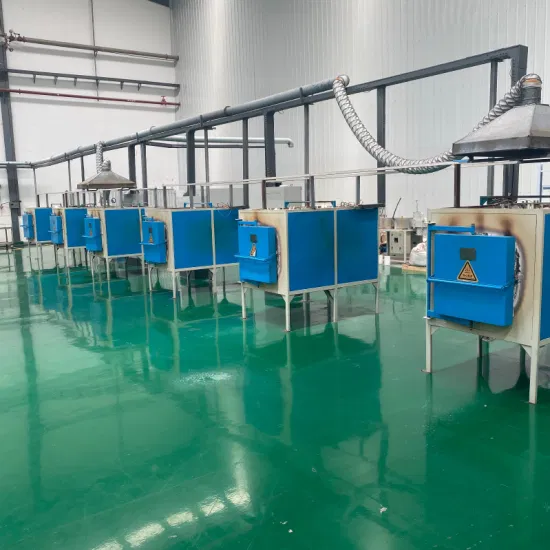
The Araxa plant of the Sao Paulo Mining and Metallurgical Company in Brazil is the largest iron niobium producer in the world. Since 1965, the traditional thermite process has been used to produce iron niobium. In the early 1990s, a semi-continuous self-thermal reduction process was established to produce iron niobium (see Figure 2). The reactor for thermite smelting is fixed (FIG. 3) and equipped with a furnace cover. The reaction produces slag with iron niobium discharged from the furnace. Load the prepared materials into the specified cylindrical silo with the tank. All kinds of charges are weighed according to the ingredients, each time loading 1/12 of the total consumption (the mixture is about 2500kg). After mixing for 4min in the mixer, it is unloaded into the small silo, and then added to the conveyor belt by the screw conveyor to the mixing silo at the top of the thermite reactor. All silo outlets are connected to an exhaust pipe through a cloth bag filter to maintain negative pressure to reduce dust. Open the mixing bin valve and add 10t of mixture to the reactor. The reaction begins when lit with magnesium strips. After the reaction of the charge, the rest of the mixture is added at 1 ~ 3t/min. After the reaction, open the slag outlet and release the slag. Slag is granulated with high pressure water. Then open the iron outlet to release niobium iron, ingots (each weight about 4t). A smelting cycle is about 1h.
Nickel niobium alloy
Used for non - ferrous alloy materials, mainly nickel - based superalloy. It is often called VQNi -- Nb. Its typical components are: Nb58.54%, Ta0.31%, A10.39%, Ti0.02%, Si0.15%, Mn0.03%, C0.03%, P0.028%, S0.004%, Fe0.53%, Ni39.18%. Because of the requirement of low impurities, it can not use niobium concentrate, but by hydrometallurgical treatment of high purity Nb2O5. High purity Nb2O5 is fine powder, to use the ball forming mechanism into a diameter of about 2mm ball, drying after use, in order to improve the yield of niobium. Smelting niobium-nickel alloy, if nickel oxide is used as raw material, is smelted by thermite, with potassium chlorate or sodium chlorate as heating agent (the operation process is the same as iron niobium). If electrolytic nickel is used as raw material, it is smelted in an electric furnace by first adding electrolytic nickel to the bottom of the furnace and then adding slag-making agent (lime) on top of it. Electricity melted metal nickel, heating power failure, adding Nb2O5 and aluminum particles, lime mixture. When the reaction is over, stir and heat. [2]
Nb ferromanganese alloy
The slag containing Nb2O5 ~ 0.5% is produced when the pig iron containing niobium is made in the open furnace of China Baotou Iron & Steel Company. This kind of flat furnace slag is smelted with iron ore in a blast furnace to obtain molten iron containing 0.7% ~ 0.8%Nb. The molten iron was put into the side blowing converter and the slag containing Nb2O54.5% ~ 6.5% was obtained. The slag of the converter is melted in the arc furnace, and some metal iron and part phosphorus are removed from the slag, and then the niobiummanganese alloy is reduced by toner. Its components are: Nb10% ~ 15%, Mn40% ~ 60%, SI0.5%-2%, C6% ~ 7%, P1.5%-2%. This alloy is used to treat niobium carbon steel.
Prev: Nano Chromium Carbide Powder 99.5% (Metals Basis)
Next: Titanium Carbide Tic Particle Used for Powder Metallurgy Production Metal Ceramic
Our Contact